Cisco CCNP Route drag and drop 2019
Here you can find all Drag and Drop questions for Cisco CCNP Route 300-101 exam. I have collected them all in one place, so you can practice lot easier. I added some new DnDs from forum. So lets start and good luck 🙂
- Drag and drop for adverse network conditions.
Answer:
Excessive unicast flooding condition: caused by including a host port in STP
Out-of-order packets: potential result of disabling FIFO
TCP starvation: potential effect of excessive UDP traffic on link
Asymmetric routing: cause of inconsistent traffic patterns
Latency: condition in which packets require an excessive length of time to traverse a switch
2. Drag drop the correct descriptions on the right to the Frame Relay LMI extensions on the left.

Answer:
+ Address registration – It allows neighboring Cisco devices to exchange management IP addresses
+ Global addressing – It enables the Frame Relay network to identify interfaces in the same manner as a LAN
+ Multicasting – It provides the most efficient transmission of routing protocol messages and supports address resolution
+ Simple flow control – It supports devices that are unable to use congestion notification
+ Virtual circuit status messages – It prevents data from being transmitted into black holes
3. Drag the descriptions on the left to the appropriate group on the right.
Answer:
Authentication:
+ supports a local database for device access
+ supports encryption
Authorization:
+ specifies a user‘s specific access privileges
+ enforces time periods during which a user can access the device
Accounting:
+ not supported with local AAA
+ verifies network usage
4. Drag drop about AAA commands.
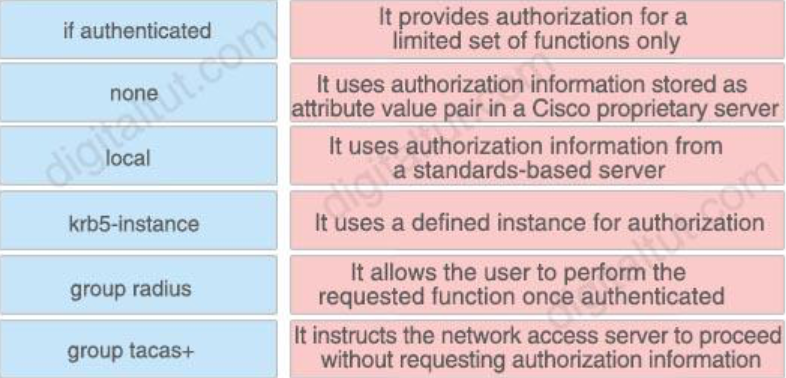
Answer:
+ if authenticated – It allows the user to perform the requested function once authenticated
+ none – It instructs the network access server to proceed without requesting authorization information
+ local – It provides authorization for a limited set of functions only
+ krb5-instance – It uses a defined instance for authorization
+ group radius – It uses authorization information from a standards based server
+ group tacas+ – It uses authorization information stored as attribute value pair in a Cisco proprietary server
5. Refer to the exhibit. You are configuring the R1 Serial0 interface for a multipoint connection. Drag and drop the required configuration statements from the left onto the corresponding locations from the diagram on the right.
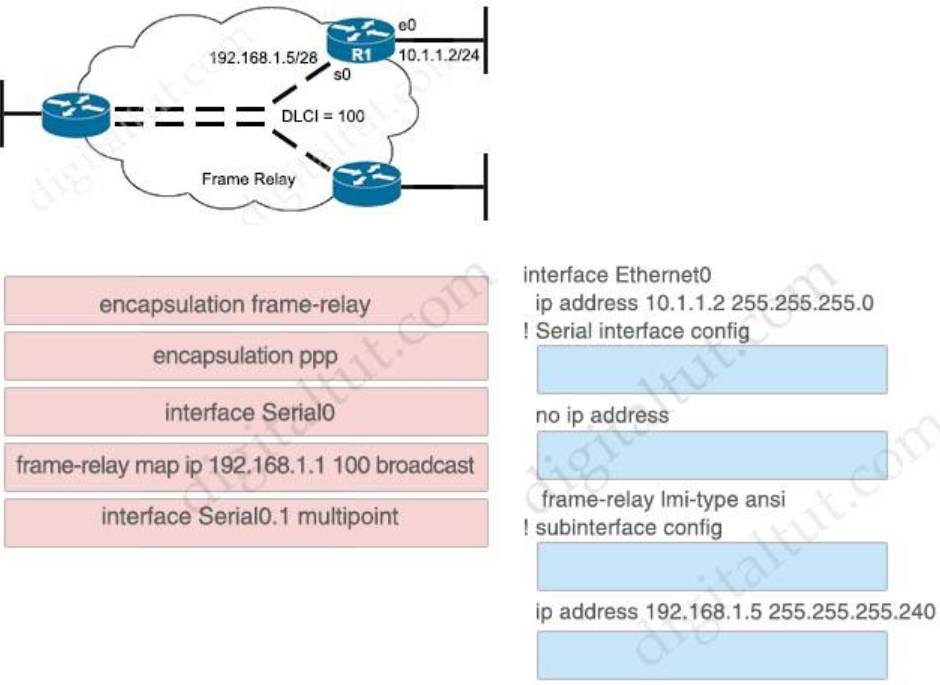
Answer:
interface Ethernet0
ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
interface Serial0
! Serial interface config
no ip address
encapsulation frame-relay frame-relay lmi-type ansi
! subinterface config
interface Serial0.1 multipoint
ip address 192.168.1.5 255.255.255.240
frame-relay map ip 192.168.1.1 100 broadcast
6. Drag and drop the GRE features from the left onto the correct description on the right.

Answer:
+ mGRE: technology that supports dynamic tunnel endpoints
+ IPSec: encryption protocol used to source tunnels
+ Keepalive: technology that prevents one side of the tunnel from going down while the other stays up
+ Tunnel Key: clear-text password that confirms the peer connection
+ MSS: configurable value that prevents an interface from sending packets that are too large for the tunnel
7. Drag and drop the AAA features from the left onto the correct description on the right.

Answer:
+ Authentication: challenge and response operation
+ Accounting: feature that logs network usage
+ TACACS+: authentication method that uses TCP
+ RADIUS: authentication method that uses UDP
+ Authorization: controls specific access privileges of a user
8. Drag and drop each statement about uRPF on the left to the correct uRPF mode on the right.

Answer:
Loose Modes:
+ It supports using the default route as a route reference
+ It requires the source address to be routable
Strict Modes:
+ It can drop legitimate traffic
+ It permits only packets that are received on the same interface as the exit interface for the destination address
9. Refer to the exhibit. You are configuring the R1 Serial0 interface for a point-to-point connection. Drag and drop the required configuration statements from the left onto the correct locations from the diagram on the right. Not all commands are used.
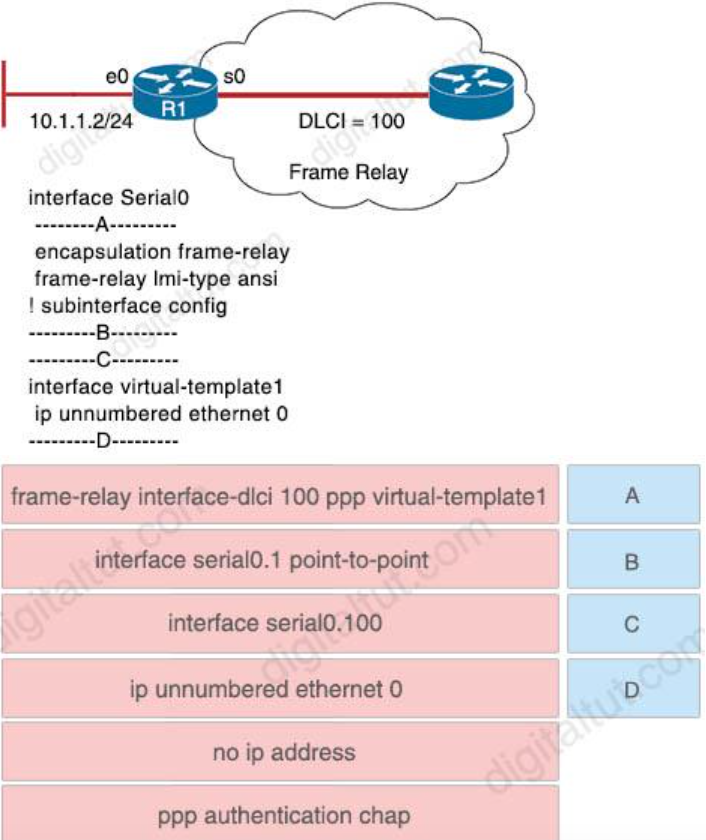
Answer:
A – no ip address
B – interface serial0.1 point-to-point
C – frame-relay interface-dlci 100 ppp virtual-template1
D – ppp authentication chap
10. Drag and drop the statements from the left onto the correct IPv6 router security features on the right.

Answer:
IPv6 Traffic Filter
+ It filters traffic on the interface level
+ It supports tagged ACLs
IPv6 Access Classes
+ It controls traffic to and from the router
+ It requires the destination address for inbound traffic to be a local address
+ It filters management traffic
11. Drag and drop the statements about device security from the left onto the correct description on the right

CoPP:
+ It protects the device against DoS attacks
+ It supports packet forwarding by reducing the load on the device
+ It uses QoS to limit the load on the device
MPP:
+ It designates the permitted management interfaces on the device
+ It is enabled only when an interface is configured
+ It requires only a single command to configure
12. Drag and drop the correct description on the right onto the corresponding ACL types on the left.

Answer:
+ Dynamic: ACL that uses Telnet for Authentication
+ Extended: ACL type that should be placed closest to the traffic source
+ Reflexive: ACL that must be defined with a named ACL
+ Standard: ACL numbered from 1300 through 1999
+ Time-based: ACL that applied to traffic only during specifically defined periods
13. Drag and drop the steps in the NAT process for IPv4-initiated packers from the left into the correct sequence on the right.
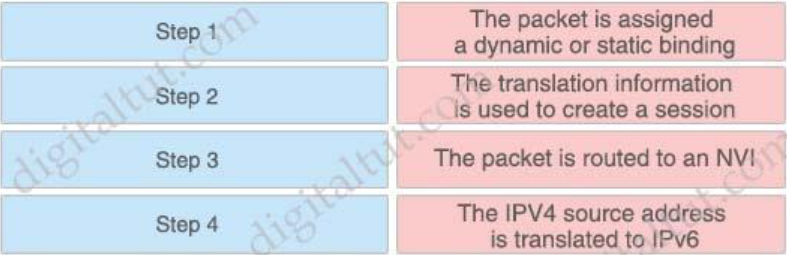
Answer:
Step 1: The packet is routed to an NVI
Step 2: The packet is assigned a dynamic or static binding
Step 3: The IPV4 source address is translated to IPv6
Step 4: The translation information is used to create a session
14. Drag the items on the left to the proper locations on the right.

Answer:
+ network-specific stateful NAT64 prefix: IPv6 prefix assigned by an organization
+ NAT64 : supports application layer gateway
+ NPTv6 : translates 2001:1::/64 to 2001:2::/64
+ well-known stateful NAT64 prefix: supports IPv6 prefix 64:FF9B::/96
15. Drag and drop the statements about NAT64 from the left onto the correct NAT64 types on the right.
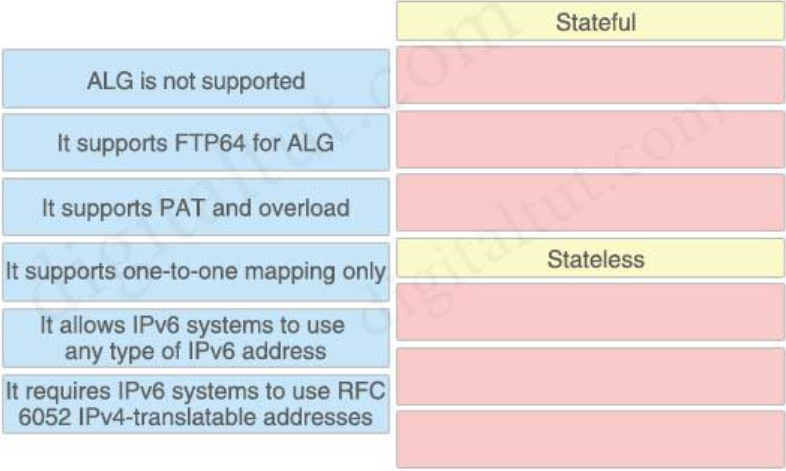
Answer:
Stateful:
+ It supports FTP64 for ALG
+ It supports PAT and overload
+ It allows IPv6 systems to use any type of IPv6 address
Stateless:
+ ALG is not supported
+ It supports one-to-one mapping only
+ It requires IPv6 systems to use RFC6052 IPv4-translatable addresses
16. Drag and drop the DMVPN components from the left onto the correct descriptions on the right.
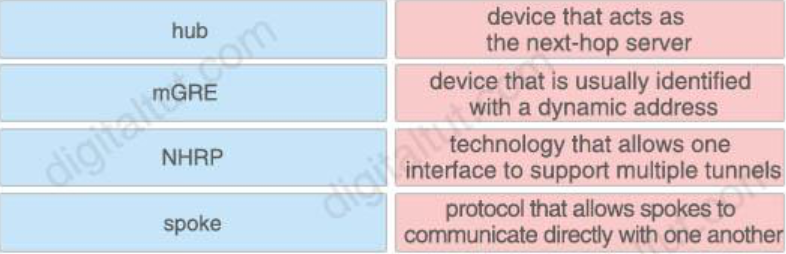
Answer:
hub – device that acts as the next-hop server
spoke – device that is usually identified with a dynamic address
mGRE – technology that allows one interface to support multiple tunnels NHRP – protocol that allows spokes to communicate directly with one another
17. NEW FROM FORUM
NO PICTURE
The question regarding the new DHCP DnD:
ip dhcp relay information option –>automatically add the circuit identifier suboption and the remote ID suboption
ip dhcp relay information check –>check that the relay agent information option in forwarded BOOTREPLY messages is valid
ip dhcp relay informatiwon policy–>Configures the reforwarding policy for a DHCP relay agent
ip dhcp relay information subscriber-id–>enable an ISP to add a unique identifier
ip dhcp relay information trusted-sources–>configures interfaces on a router as trusted sources
ip dhcp relay information–> configured in global configuration mode applies to all interfaces
18. NEW FROM FORUM
NAT64:
+ Use Network-specific prefix
+ Modify session during translation
NPTv6:
+ Modify IP header in transit
+ Map one IPv6 address prefix to another IPv6 prefix
19. NEW FROM FORUM
+ OpenSent: wait for an OPEN message
+ OpenConfirm: wait for a KEEPALIVE or NOTIFICATION message
+ Established: UPDATE, NOTIFICATION and KEEPALIVE messages are exchanged with peers
+ Idle: refuse connections
+ Active: listen for and accept connection
+ Connect: wait for the connection to be completed
20. NEW FROM FORUM
+ Target 1: When the LCP phase is complete and CHAP is negotiated between both devices, the authenticator sends a challenge message to the peer
+ Target 2: The peer responds with a value calculated through a one-way hash function (MD5)
+ Target 3: The authenticator checks the response against its own calculation of the expected hash value if the values match the authentication is successful. Otherwise, the connection is terminated
21. NEW FROM FORUM
+ SVC: A circuit that provides temporary on-demand connections between DTEs
+ LMI: A signaling mechanism for Frame Relay devices
+ DLCI: A locally significant ID
+ FECN: An indicator edof congestion on the network
+ PVC: A logical connection comprising two endpoints and a CIR
NEW FROM FORUM January 10th, 2019
New “AAA Accounting” drag & drop:
Answer:
1. Auth-proxy: It returns information about hosts using proxy service
2. Commands: It returns information about individual EXEC commands and permissions associated with a privilege level.
3. Connection: It returns information about outbound communications from the network access server
4. Exec: It returns information about user EXEC terminal sessions with the network access server
5. Network: It returns information about SLIP, PPP and ARA sessions.
6. Resources: It returns information about calls that have passed and failed user authentication
 Umrežen Blog Blog o umrežavanju i internetu. Tutorijali, SpeedTest, Merenje Brzine interneta, Telekom ADSL, Telenor, VIP, Sbb, Orion.
Umrežen Blog Blog o umrežavanju i internetu. Tutorijali, SpeedTest, Merenje Brzine interneta, Telekom ADSL, Telenor, VIP, Sbb, Orion.

